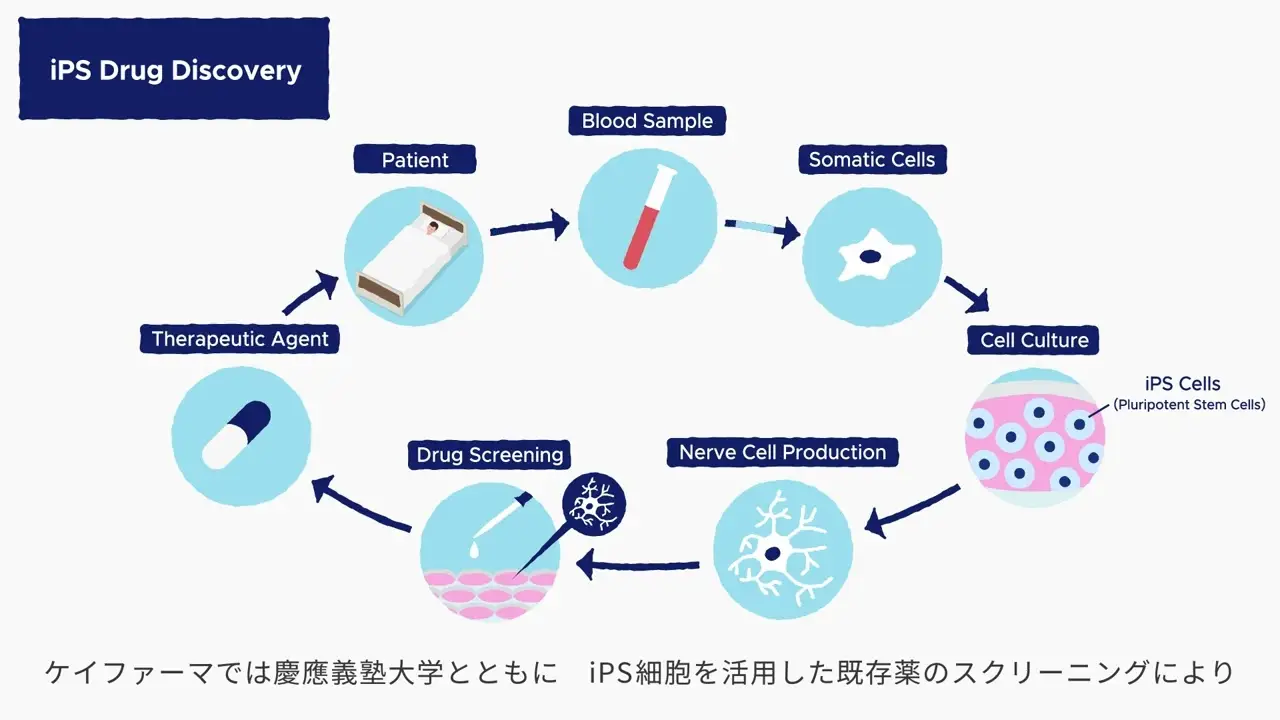
iPS drug discovery

What are iPS cells?
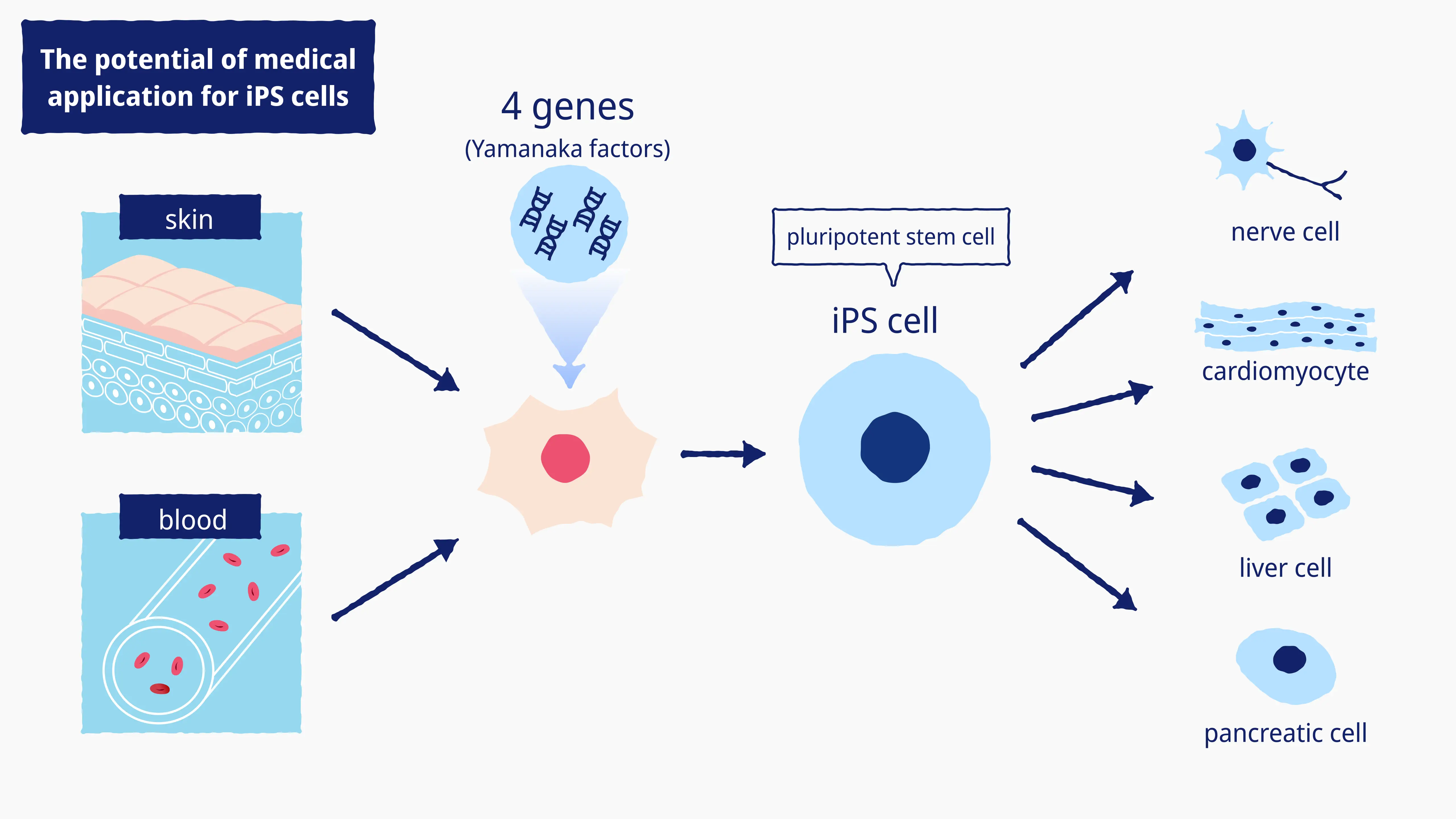
iPS (induced pluripotent stem) cells are typically produced from blood and skin cells. Researchers in Japan and around the world have been working on iPS cells ever since the first cells were successfully produced by Professor Shinya Yamanaka at Kyoto University in August 2006. iPS cells can be differentiated to produce a variety of cell and tissue types. This makes them ideal for regenerative medicine, the science of regenerating tissue and internal organs lost through disease or mishap. iPS cells can also be cultured directly from patient samples to reproduce diseased cells for use in researching pathological mechanisms and developing drug treatments.
What is iPS drug discovery?
Cutting-edge drug discovery research using iPS cells
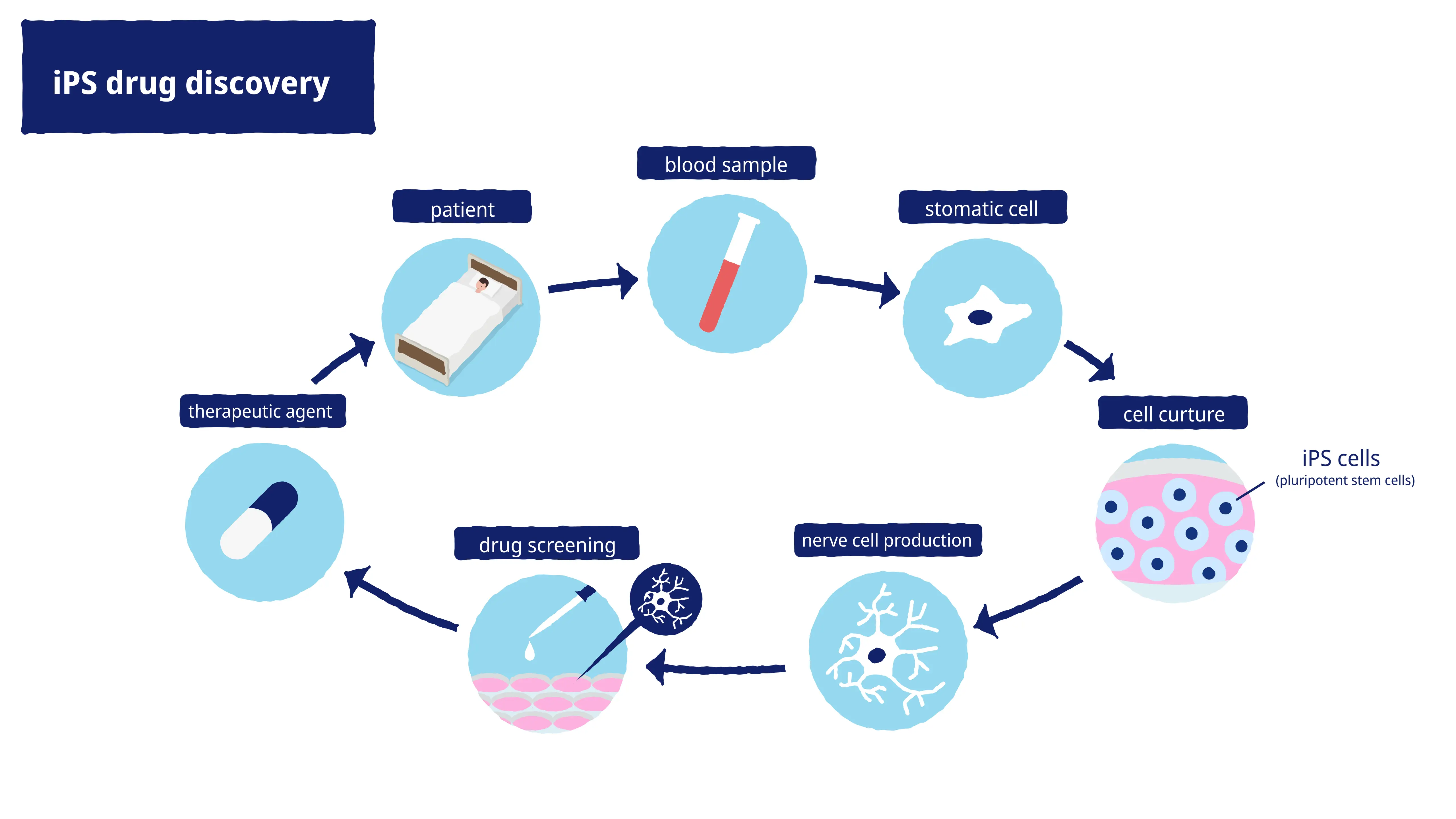
iPS drug discovery refers to the use of disease-specific iPS cells derived from patient samples in developing new therapeutic agents and treatments. iPS cells can be differentiated to produce a variety of cell and tissue types, which enables us to develop pathological (disease) models involving cells with disease-specific characteristics. To date, drug discovery in connection with rare diseases has been constrained by insufficient patient numbers, but with the advent of iPS cells, we are now in a much better position to pursue research on new therapeutic treatments.
Main disease areas
Learn about the diseases we are tackling through iPS drug discovery.
-
Neurological diseases
Neurological diseases are diseases that involve damage to the brain, spinal cord and/or nerves, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer’s disease.
Business environment
Learn about the latest developments in the domestic and global pharmaceutical industry.
What is drug repositioning?
Development of new therapeutic agents normally takes a decade or two, which represents an enormous financial investment. In the case of intractable diseases, there are additional constraints such as insufficient numbers of patients for clinical trials. Our approach at K Pharma involves the use of drug repositioning—the process of reconfiguring an existing drug—as part of the iPS drug discovery process. The aim is to identify a suitable existing drug that is known to be effective for a given disease, then reconfigure it to treat a different disease. K Pharma uses patient samples (typically blood cells) to produce iPS cells that in turn yield specialized cells for targeted research via the process of differentiation-induction. This approach is significantly faster and cheaper than the traditional drug discovery process.

Development focus
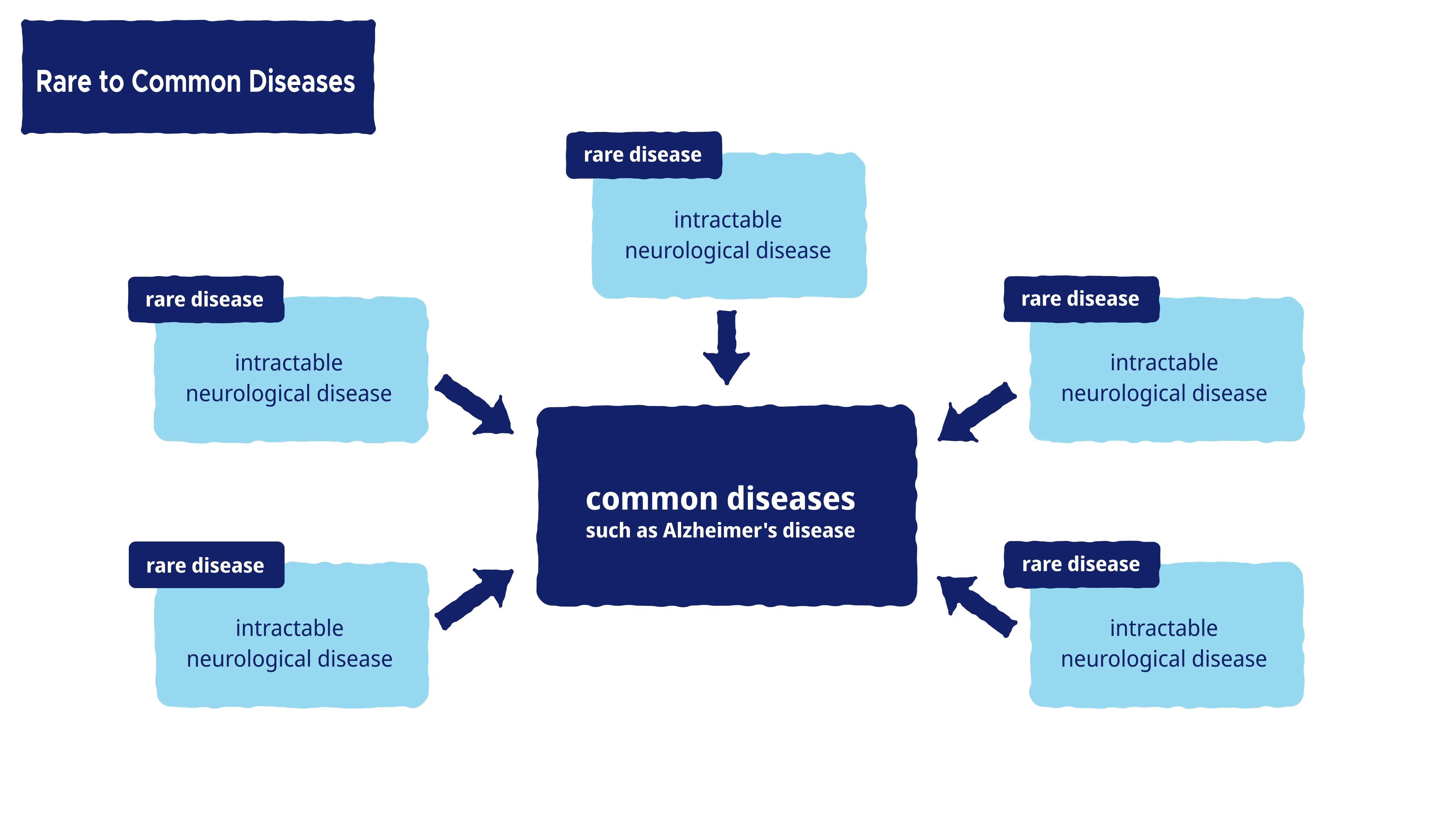
Rare to Common Diseases
At K Pharma, we channel our research findings on specific rare diseases into the development of therapeutic treatments for other, more common diseases, as part of our mission to assist the greatest possible number of people.
This video describes our work in iPS drug discovery and regenerative medicine.